Alcyone Software
Alcyone Astronomical Tables: List of Available Tables
Software > Alcyone Astronomical Tables
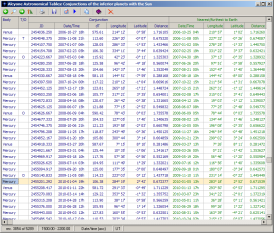
Conjunctions of the inferior planets with the Sun
This table contains information on all inferior and superior conjunctions of Mercury and Venus with the Sun taking place from -2998 to 2999. For each conjunction the following data are given:
- instant of conjunction as a Julian day number and as a Julian/Gregorian calendar date
- time difference between the current and preceding conjunction of the body
- geocentric ecliptical longitude and latitude of the planet at the time of conjunction
- geocentric distance of the planet at the time of conjunction
- instant of the planet's least (inferior conjunctions) or greatest (superior conjunctions) geocentric distance
- geocentric ecliptical longitude and latitude of the planet at the time of the its least or greatest geocentric distance
- greatest or least geocentric distance of the planet
- instant when the planet begins to move westward (retrograde, first station in celestial longitude) as a Julian day number and as a Julian/Gregorian calendar date
- geocentric ecliptical longitude and latitude of the planet at the instant of first station
- time difference (in days) between the instant of first station and succeeding conjunction
- instant when the planet resums direct motion (eastward, second station in celestial longitude) as a Julian day number and as a Julian/Gregorian calendar date
- geocentric ecliptical longitude and latitude of the planet at the instant of second station
- time difference (in days) between the instant of second station and preceeding conjunction
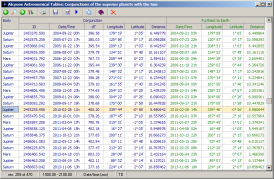
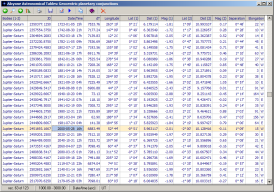
Conjunctions of the superior planets with the Sun
This table contains information on all conjunctions of Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, and Uranus with the Sun taking place from -2998 (1700 for Uranus) to 2999. For each conjunction the following data are given:
- instant of conjunction as a Julian day number and as a Julian/Gregorian calendar date
- time difference between current and preceding conjunction of the body
- geocentric ecliptical longitude and latitude of the planet at the time of conjunction
- geocentric distance of the planet at the time of conjunction
- instant of the planet's greatest geocentric distance as a Julian/Gregorian calendar date
- geocentric ecliptical longitude and latitude of the planet at the time of the its greatest geocentric distance
- greatest distance of the planet
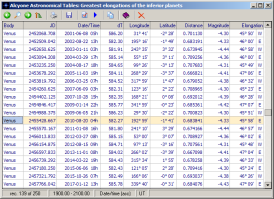
Greatest elongations of the inferior planets
This table contains information on all greatest elongations (the maximum angular distance between the planet and the center of the Sun's disk) of Mercury and Venus taking place from -2998 to 2999. For each greatest elongation the following data are given:
- instant of greatest elongation as a Julian day number and as a Julian/Gregorian calendar date
- time difference between current and preceding greatest elongation of the body
- geocentric ecliptical longitude and latitude of the planet at the time of greatest elongation
- geocentric distance of the planet at the time of greatest elongation
- apparent visiual magnitude of the planet at the time of greatest elongation
- greatest elongation of the planet (angular separation between the planet and the center of the Sun's disk)
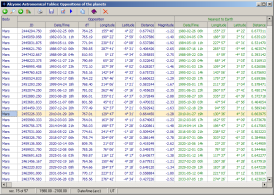
Oppositions of the planets
This table contains information on all oppositions of Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, and Uranus taking place from -2998 (1700 for Uranus) to 2999. For each opposition the following data are given:
- instant of opposition as a Julian day number and as a Julian/Gregorian calendar date
- time difference between current and preceding opposition of the body
- geocentric ecliptical longitude and latitude of the planet at the time of opposition
- geocentric distance of the planet at the time of opposition
- apparent visiual magnitude of the planet at the time of opposition
- geocentric ecliptical longitude and latitude of the planet at the time of the its least geocentric distance
- least geocentric distance of the planet
- instant when the planet begins to move westward (retrograde, first station in celestial longitude) as a Julian day number and as a Julian/Gregorian calendar date
- geocentric ecliptical longitude and latitude of the planet at the instant of first station
- time difference (in days) between the instant of first station and succeeding conjunction
- instant when the planet resums direct motion (eastward, second station in celestial longitude) as a Julian day number and as a Julian/Gregorian calendar date
- geocentric ecliptical longitude and latitude of the planet at the instant of second station
- time difference (in days) between the instant of second station and preceeding conjunction
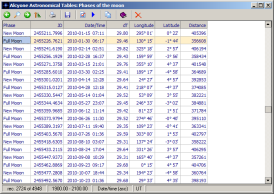
Phases of the Moon
This table contains information on the instants of the phases of the moon for the years -2998 to 2999. These are the instants when the difference between the apparent longitudes of the moon and the sun (corrected for the effects of aberration and nutation) is 0° (New moon), 90° (First quarter), 180° (Full moon), or 270° (Last quarter). For each lunar phase the following data are given:
- instant of lunar phase as a Julian day number and as a Julian/Gregorian calendar date
- time difference between current and preceding lunar phase of the same kind
- geocentric ecliptical longitude and latitudes of the Moon
- geocentric distance of the Moon
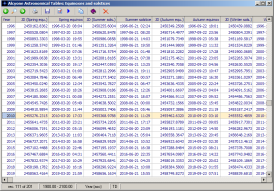
Equinoxes and solstices
This table contains information on the times of equinoxes and solstices for the years -2998 to 2999. These are the instants when the apparent longitude of the sun (corrected for the effects of aberration and nutation) is 0° (spring equinox), 90° (summer solstice), 180° (autumn equinox), or 270° (winter solstice).
Geocentric planetary conjunctions
This table contains information on all geocentric planetary conjunctions in celestial longitude between Mercury, Venus, Mars, Jupiter, and Saturn taking place from -2998 to 2999. For each on the following data are given:
- instant of conjunction as a Julian day number and as a Julian/Gregorian calendar date
- time difference between current and preceding conjunction of the bodies
- geocentric ecliptical longitude and latitudes of the planets at the time of conjunction
- geocentric distances of the planets at the time of conjunctions
- apparent visiual magnitude of the planets at the time of conjunction
- angular separation between the bodies at the time of conjunction
- elongation from Sun at the time of conjunction (rounded to nearest degree)
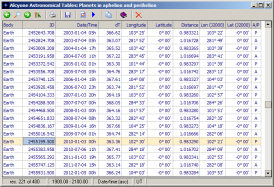
Planets in aphelion and perihelion
This table contains information on all aphelion and perihelion passages of Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune taking place from -2998 to 2999. For each passage the following data are given:
- instant of passage as a Julian day number and as a Julian/Gregorian calendar date
- time difference between current and preceding aphelion/perihelion passage of the body
- heliocentric ecliptical longitude and latitude of the planet at the time of aphelion/perihelion passage referred to the mean equinox of the date and to the mean equinox of J2000
- heliocentric distance of the planet at the time of aphelion/perihelion passage
Five Millennium Canon of Solar Eclipses
This table contains information on all solar eclipses taking place from -1999 to +3000. All eclipse predictions were performed by Fred Espenak and Jean Meeus ( NASA's GSFC). For each eclipse the following data are given:
- The sequential number of the eclipse in the Five Millennium Canon of Solar Eclipses.
- The date at instant of greatest eclipse (the instant when the axis of the Moon's shadow cone passes closest to Earth's center) as a Julian day number and as a calendar date in ephemeris time or universal time.
- The lunation number (number of synodic moons since New Moon of 2000-01-06).
- The Saros series number of eclipse.
- The type of eclipse (total, annular, hybrid, partial).
- Distance of the shadow cone axis from the center of Earth (in units of equatorial Earth radii) at the instant of greatest eclipse.
- Eclipse magnitude (fraction of the Sun's diameter obscured by the Moon). For annular, total, and hybrid eclipses this value is actually the diameter ration of Moon/Sun.
- Geographic latitude and longitude where greatest eclipse is seen.
- Sun's altitude and azimuth at greatest eclipse.
- Width of the path of totality or annularity at greatest eclipse in kilometers.
- Central line duration of total or annular phase at greatest eclipse.
Five Millennium Canon of Lunar Eclipses
This table contains information on all lunar eclipses taking place from -1999 to +3000. All eclipse predictions were performed by Fred Espenak and Jean Meeus ( NASA's GSFC). For each eclipse the following data are given:
- The sequential number of the eclipse in the Five Millennium Canon of Lunar Eclipses.
- The date at instant of greatest eclipse (the instant when the distance between the center of the Moon and the axis or Earth's umbral shadow cone reaches a minimum) as a Julian day number and calendar date in ephemeris time or universal time.
- The lunation number (number of synodic moons since New Moon of 2000-01-06).
- The Saros series number of eclipse.
- The type of eclipse (total, partial, penumbral).
- Penumbral magnitude (fraction of the Moon's diameter immersed in the penumbra at the instant of greatest eclipse).
- Umbral magnitude (fraction of the Moon's diameter immersed in the penumbra at the instant of greatest eclipse).
- Distance from the center of the shadow cone axis to the center of the Moon (in units of Earth's equatorial radii) at the instant of greatest eclipse.
- Duration of penumbral phase of a lunar eclipse (in minutes); equal to the time interval between first and last contact of the Moon with the penumbral shadow.
- Duration of partial phase of a lunar eclipse (in minutes); equal to the time interval between first and last contact of the Moon with the umbral shadow
- Duration of total phase of a lunar eclipse (in minutes); equal to the time interval between second and third contact of the Moon with the umbral shadow
- Quincena Solar Eclipse Parameter. Identifies the type of solar eclipse that precedes and/or succeeds a lunar eclipse. Solar eclipse types: p = partial solar eclipse (Moon's penumbral shadow traverses Earth), a = annular solar eclipse (Moon's antumbral shadow traverses Earth), t = total solar eclipse (Moon's umbral shadow traverses Earth). h = hybrid solar eclipse (Moon's umbral and antumbral shadows traverse different parts of Earth).
- Geographic latitude and longitude where the Moon appears in the zenith at instant of greatest eclipse.